在搭建 NKCTF 网站的时候学习到的有关 UWSGI 的知识
WSGI协议
几个概念:
- WSGI:Web Server Gateway Interface。
WSGI不是服务器,python模块,框架,API或者任何软件,只是一种规范,描述web server如何与web application通信的规范。WSGI server负责从客户端接收请求,将request转发给application,将application返回的response返回给客户端;WSGI application接收由server转发的request,处理请求,并将处理结果返回给server。application中可以包括多个栈式的中间件(middlewares),这些中间件需要同时实现 server 与 application,因此可以在 WSGI 服务器与 WSGI 应用之间起调节作用:对服务器来说,中间件扮演应用程序,对应用程序来说,中间件扮演服务器。
- **uwsgi:**与
WSGI一样是一种通信协议,是uWSGI服务器的独占协议,用于定义传输信息的类型,每一个uwsgi packet前4byte为传输信息类型的描述,与WSGI协议是两种东西,据说该协议是fcgi协议的10倍快。(快速通用网关接口 → Fast Common Gateway Interface/FastCGI)是一种让交互程序与Web服务器通信的协议) - **uWSGI:**是一个
web服务器,实现了WSGI协议、uwsgi协议、http协议等。
WSGI协议的实现
以 Django 为例,分析一下 WSGI 协议的具体实现过程:
django WSGI application
application 的流程包括:
- 加载所有中间件,以及执行框架相关的操作,设置当前线程脚本前缀,发送请求开始信号;
- 处理请求,调用
get_response()方法处理当前请求,该方法的的主要逻辑是通过urlconf找到对应的view和callback,按顺序执行各种middleware和callback。 - 调用由
server传入的start_response()方法将响应header与status返回给server。 - 返回响应正文
django WSGI Server
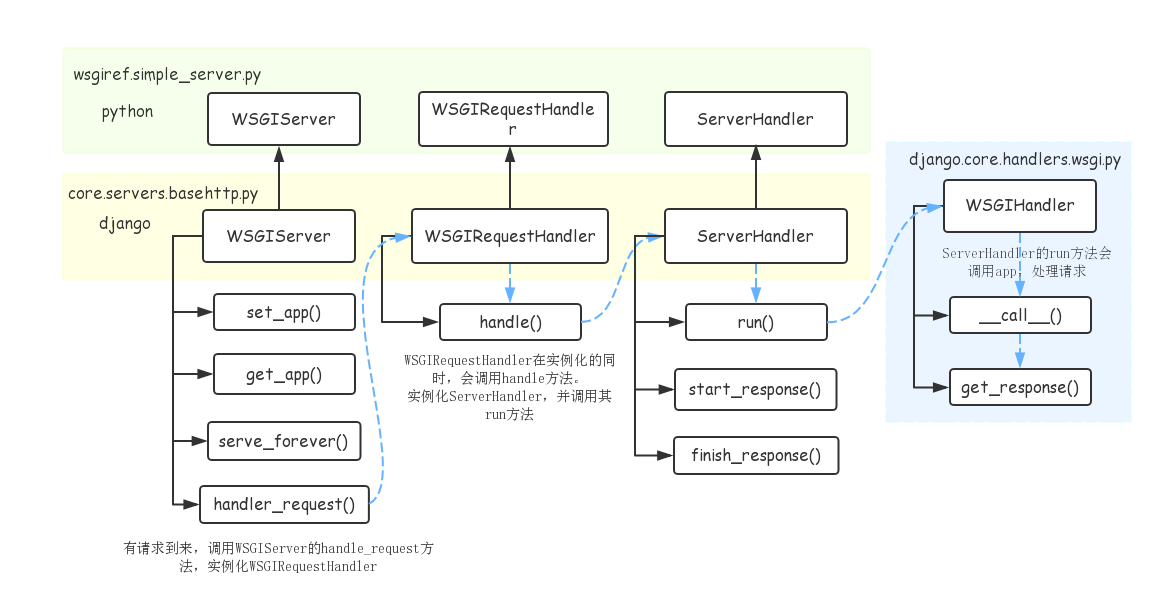
通过 python manage.py runserver 运行 django 项目,在启动时都会调用下面的 run 方法,创建一个 WSGIServer 的实例,之后再调用其 serve_forever() 方法启动服务。
| |
下面表示 WSGI server 服务器处理流程中关键的类和方法:
UWSGI
uwsgi 命令行
强制停止后台的所有 uwsgi 进程:
| |
uwsgi 配置
见:https://uwsgi-docs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Configuration.html
uWSGI configuration files can include “magic” variables, prefixed with a percent sign. Currently the following magic variables (you can access them in Python via uwsgi.magic_table) are defined:
| %v | the vassals directory (pwd) |
|---|---|
| %V | the uWSGI version |
| %h | the hostname |
| %o | the original config filename, as specified on the command line |
| %O | same as %o but refer to the first non-template config file (version 1.9.18) |
| %p | the absolute path of the configuration file |
| %P | same as %p but refer to the first non-template config file (version 1.9.18) |
| %s | the filename of the configuration file |
| %S | same as %s but refer to the first non-template config file (version 1.9.18) |
| %d | the absolute path of the directory containing the configuration file |
| %D | same as %d but refer to the first non-template config file (version 1.9.18) |
| %e | the extension of the configuration file |
| %E | same as %e but refer to the first non-template config file (version 1.9.18) |
| %n | the filename without extension |
| %N | same as %n but refer to the first non-template config file (version 1.9.18) |
| %c | the name of the directory containing the config file (version 1.3+) |
| %C | same as %c but refer to the first non-template config file (version 1.9.18) |
| %t | unix time (in seconds, gathered at instance startup) (version 1.9.20-dev+) |
| %T | unix time (in microseconds, gathered at instance startup) (version 1.9.20-dev+) |
| %x | the current section identifier, eg. config.ini:section (version 1.9-dev+) |
| %X | same as %x but refer to the first non-template config file (version 1.9.18) |
| %i | inode number of the file (version 2.0.1) |
| %I | same as %i but refer to the first non-template config file |
| %0..%9 | a specific component of the full path of the directory containing the config file (version 1.3+) |
| %[ | ANSI escape “\033” (useful for printing colors) |
| %k | detected cpu cores (version 1.9.20-dev+) |
| %u | uid of the user running the process (version 2.0) |
| %U | username (if available, otherwise fallback to uid) of the user running the process (version 2.0) |
| %g | gid of the user running the process (version 2.0) |
| %G | group name (if available, otherwise fallback to gid) of the user running the process (version 2.0) |
| %j | HEX representation of the djb33x hash of the full config path |
| %J | same as %j but refer to the first non-template config file |